Lathe Works
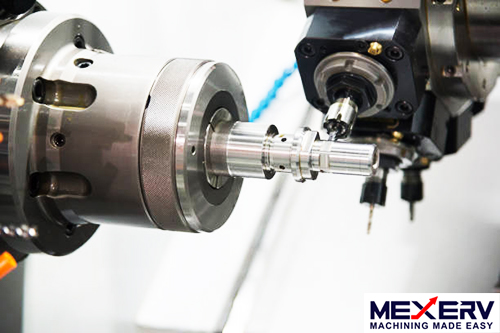
The Lathe machine is commonly known as the "Mother of Machining Tools”. It can be used for a variety of machining purposes.
Technically, a lathe is a machine tool which can be used to remove or shave-off unwanted metals from the work piece to give desired shape and size. A Lathe machine operates on the principle of a rotating work piece and a fixed cutting tool. It operates on the principle of a rotating work piece and a fixed cutting tool. The cutting tool is fed into the workpiece which rotates about its own axis causing the workpiece to form the desired shape. The main parts of a lathe are the bed, headstock, tailstock, spindles, toolrest, and motor. Lathe machines are among one of the most important machine tools which are used in the metal-working industry.
Machine Types
- Engine lathe or center lathe
- Bench lathe
- Speed lathe
- Tool room lathe
- Special purpose lathe
Specifications
| Number of Spindle Speeds | 6 |
|---|---|
| Number of Spindle Speeds | Induction Hardened Bed Way |
| Size | 3.5 Feet | 4.5 Feet | 5.3 Feet | 6 Feet | 7 Feet |
| Layout | Horizontal |
| Admit Between Centre | 190 mm | 500 mm | 725 mm | 950 mm | 1250 mm |
| Lead Screw Diameter Or Pitch | 4 TPI & 32 mm Die |
| Suitable Electrical Hp | 2 HP |
| Bed width | 275 mm |
| Distance Of Between Center | 500 mm | 725 mm | 950 mm |
| Height of center | 215 mm OR 254 mm |
| Spindle Bore | 50 mm OR 80 mm |
Lathe Accessories
- Work-holding, -supporting, and –driving devices
- Lathe centers, chucks, faceplates
- Mandrels, steady and follower rests
- Lathe dogs, drive plates
- Cutting-tool-holding devices
- Straight and offset toolholders
- Threading toolholders, boring bars
- Turret-type toolposts
Cutting Tool Material Specifications
Carbon tool steel
Carbon steel tool is used in twist drills, milling tools, turning and forming tools, used for soft material such as brass, aluminum magnesium, etc.
- Temperature - 450°C
- Hardness – up to HRC 65
High Speed Tool Steel
- Surface treatment used in the HSS
- Super finishing - Reduce friction
- Nitriding - Increase wear resistance
- Chromium electroplating - Reduce friction
- Oxidation - Reduce friction
- Cutting speed range - 30-50 m/min
- Temperature - 650°C
- Hardness – up to HRC 67
- T-Type - Tungsten predominant type
- M-Type - Molybdenum dominant type
Cubic Boron Nitride
Cemented carbide tools are extremely hard; they can withstand very high-speed cutting operation. Carbide tool does not lose their hardness up to 1000° C. A high cobalt tool is used for a rough cut while low cobalt tool used for finishing operations.
- Cutting speed range - 60-200m/min
- Temperature - 1000°C
- Hardness – up to HRC 90
Cemented Carbide Tool
It is the second hardest material after diamond. They are generally used in hand machines. They offer high resistance to abrasion and use as an abrasive in grinding wheels. Sharp edges are not recommended.
- Speed 600-800m/min
- Hardness - higher than HRC 95
Diamond
It is the hardest material known and it is also expensive. It possesses very high thermal conductivity and melting point. Diamond offers excellent abrasion resistance, low friction coefficient and low thermal expansion. It is used in machining very hard material such as carbides, nitrides, glass, etc. Diamond tools give a good surface finish and dimensional accuracy. They are not recommended for machining steel.
Some of the common lathe operations we provide are:
- Drilling
- Reaming
- Boring
- Counter boring
- Taper boring
- Tapping
- Undercutting
- Internal thread cutting
- Parting-off
- Turning Operation
- Plain or Straight Turning
- Rough Turning
- Shoulder Turning
- Taper Turning
- Eccentric Turning
- Facing Operation
- Chamfering Operation
- Knurling Operation
- Thread cutting Operation
- Filing Operation
- Polishing Operation
- Grooving Operation
- Spinning Operation
- Spring Winding
- Forming
